 The CPU and Primary Storage
The CPU and Primary Storage
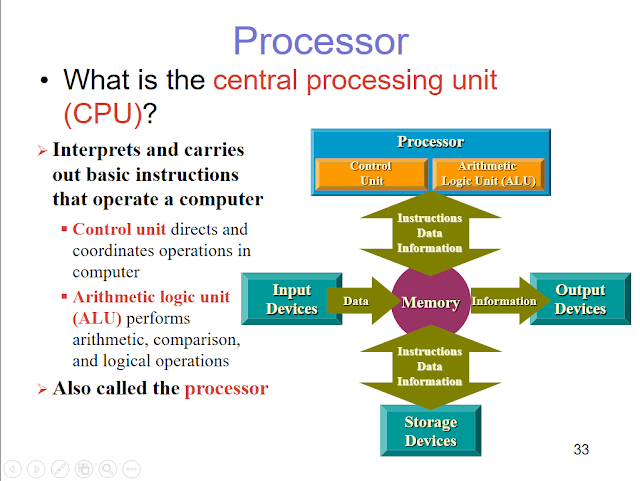
• The CPU is the part of the computer system where the manipulation of symbols, numbers, and letters occurs, and it controls the other parts of the computer system.
• Three kinds of busses linked between the CPU, primary storage and the other devices in the computer system:
– Data bus
• Pass information in bi-directional.
– Address bus
• Transmits signals for locating a given address in primary storage, indicating where data should be placed.
– Control bus
• Transmits signal specifying whether to read or write data to or from primary storage address, input device or output device.
• The characteristics of the CPU and primary storage are very important in determining a computer’s speed and capabilities
The Arithmetic-Logic Unit and Control Unit
• An arithmetic logic unit (ALU) and control unit is one of the core components of all central processing units.
• The ALU performs the computer’s principal logical and arithmetic operations.
• It adds, subtracts, multiples, and divides, determining whether a number is positive, negative, or zero.
• ALU must be able to determine when one quantity is greater than or less than another and when two quantities are equal.
• The control unit coordinates and controls the other parts of the computer system.
• It reads a stored program, one instruction at a time and directs other components of the computer system to perform the program’s required tasks.
Processor
• Which processor should you select?
• The faster the processor, the more expensive the computer
Primary Storage
• Primary storage is a category of computer storage, often called main memory.
• Has three functions:
– Stores all or part of the program that is being executed.
– Stores the operating system programs that manage the operation of the computer.
– Holds data that the program is using.
• Data and program are placed in primary storage before processing, between processing steps and after processing has ended prior to being returned to secondary storage or released as output.
Memory
• How is memory measured?
• By number of bytes available for storage
• Modern primary storage devices include:
– Random access memory (RAM)
• is used for short-term storage of data or program instructions. RAM is volatile. Its contents will be lost when the computer’s electric supply is disrupted by a power outage or when the computer turned off.
– Read-only memory (ROM)
• can only be read from. It cannot be written to. ROM chips come from the manufacturer with programs already burned in, or stored. ROM is used in general-purpose computers to store important or frequently used programs, such as computing routine for calculating the square roots of numbers.








Post A Comment:
0 comments so far,add yours