Different Approaches to Improving Information Systems Development
Several different approaches have been developed in the continuous effort to improve the systems analysis and design process. The two important approaches are prototyping and joint application development (JAD).
Prototyping
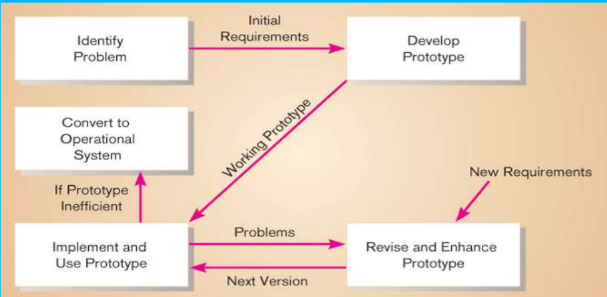
Prototyping is a form of rapid application development (RAD). Prototyping is a rapid, iterative, and incremental process of systems development in which requirements are converted to a working system that is continually revised through close work between the development team and the users. We can build a prototype with any computer language or development tool, but special prototyping tools have been developed to simply the process. A prototype can be developed with some fourth-generation language (4GL), with the query and screen and report design tools of a database management system, and with tools called computer-aided software engineering (CASE) tools.
 |
| Prototyping |
In prototyping, the analyst works with users to determine the initial or basic requirements for the system. The analyst then quickly builds a prototype. When the prototype is completed, the users work with it and tell the analyst what they like and do not like about it. The analyst uses this feedback to improve the prototype and takes the new version back to the users. This iterative process continues until the users are relatively satisfied with what they have seen.
Ideally, the prototype serves as a mechanism for identifying information system requirements. In this case, we throw away the prototype (also called throwaway prototype) after identifying requirements. The actual information system is developed with an eye toward quality and maintainability based on the requirements.
Advantages:
- Useful for projects in which user requirements are uncertain or imprecise.
- It encourages active user and management participation.
- Projects have higher visibility and support because of the extensive user involvement.
- Users and management see working, software-based solutions more rapidly.
- Errors and omissions tend to be detected earlier in prototypes.
- Testing and training are natural by-products.
- It is more natural process.
- It is most popular for small to medium-size projects.
Disadvantages:
- It increases lifetime cost to operate, support and maintain the system.
- It can solve the wrong problems since problem analysis is abbreviated or ignored.
- The product may have less quality because of speed in development.
Post A Comment:
0 comments so far,add yours